SQL Join Types - Inner Join VS Outer Join
In a relational database, all infomation should only be present once. But you might have infomation that's seperated into different tables that's related to each other.
What is a JOIN in SQL
The JOIN operator lets you combine related information in various ways. There are types of JOIN, divided into two main catergories - INNER joins and OUTER joins.
The biggest difference between an INNER JOIN and an OUTER JOIN is that the inner join will keep only the information from both tables that's related to each other(in the resulting table). An OUTER JOIN, on the other hand, will also keep information that's not related to the other table in the resulting table.
INNER JOIN
The INNER JOIN will keep only the information from the two joined tables that is related. If you imagine the two tables as Venn diagram, the table resulting from an INNER JOIN will be the green highlighted part below where they overlap:
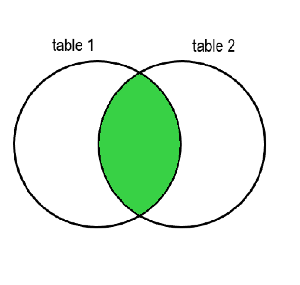
OUTER JOIN
If you want to keep all the data, and not just the data related to each other, you can use an OUTER JOIN.
There are three types of OUTER JOIN: LEFT OUTER JOIN, RIGHT OUTER JOIN, and FULL OUTER JOIN. The differences between them involve which unrelated data they keep - it can be from the first table, from the second or from both of them. The cell without data to fill will have a value of NULL.
LEFT JOIN is the mostly universally implemented in all versions of SQL. But this is not the case for RIGHT JOIN and FULL JOIN, which are not implemented in various SQL versions.
LEFT OUTER JOIN
The LEFT OUTER JOIN, or simply LEFT JOIN, will keep the unrelated data from the left(the first) table.
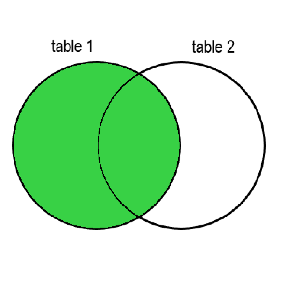
RIGHT OUTER JOIN
The RIGHT OUTER JOIN, or simply Right Join, will keep the data in the second table that's not related to the first table.
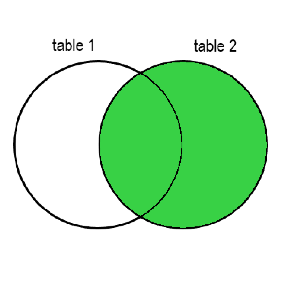
FULL OUTER JOIN
You can think of the FULL OUTER JOIN as the combination of a Left Join and Right Join. It will keep all rows from both tables, and the missing data will be filled in with NULL.
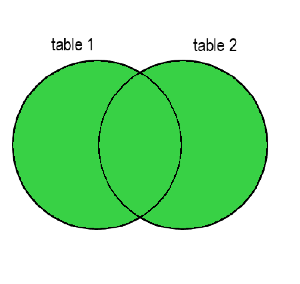
Conclusion
In a relational database, all data should be written once. To then analyse these data, you may need to use different types of JOIN operator to join some related data tables together to analyse.